We believe each child with a physical condition or a developmental disability is unique in their strengths and challenges. No matter the condition, neuromotor, neuromuscular, or orthopedic, at CYP, we build on your child’s strengths and identify areas of need to help them achieve their goals.
Physical & Developmental Conditions
Cerebral Palsy
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Developmental Coordination Disorder
Juvenile Arthritis
Muscular Dystrophy
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Down Syndrome
Charcot Marie Tooth
Brain Injury
Tethered Spinal Cord
Brachial Plexus Injury
Spina Bifida
Stroke
Global Developmental Delay
Genetic Disorders
Orthopedic conditions like club foot and Blount's disease
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is the most common motor disability in childhood. It is a general term that describes a group of disorders that affect the normal development of movement and posture. CP is caused by an injury to an infant’s developing brain. Though the damage doesn’t worsen, symptoms can change with growth and development over time. Difficulties from CP can range from mild to severe. The physical therapist will provide care at different stages in the individual’s development, depending on their unique needs. The CYP team has a lot of experience treating children with CP and we are an important partner in their healthcare.
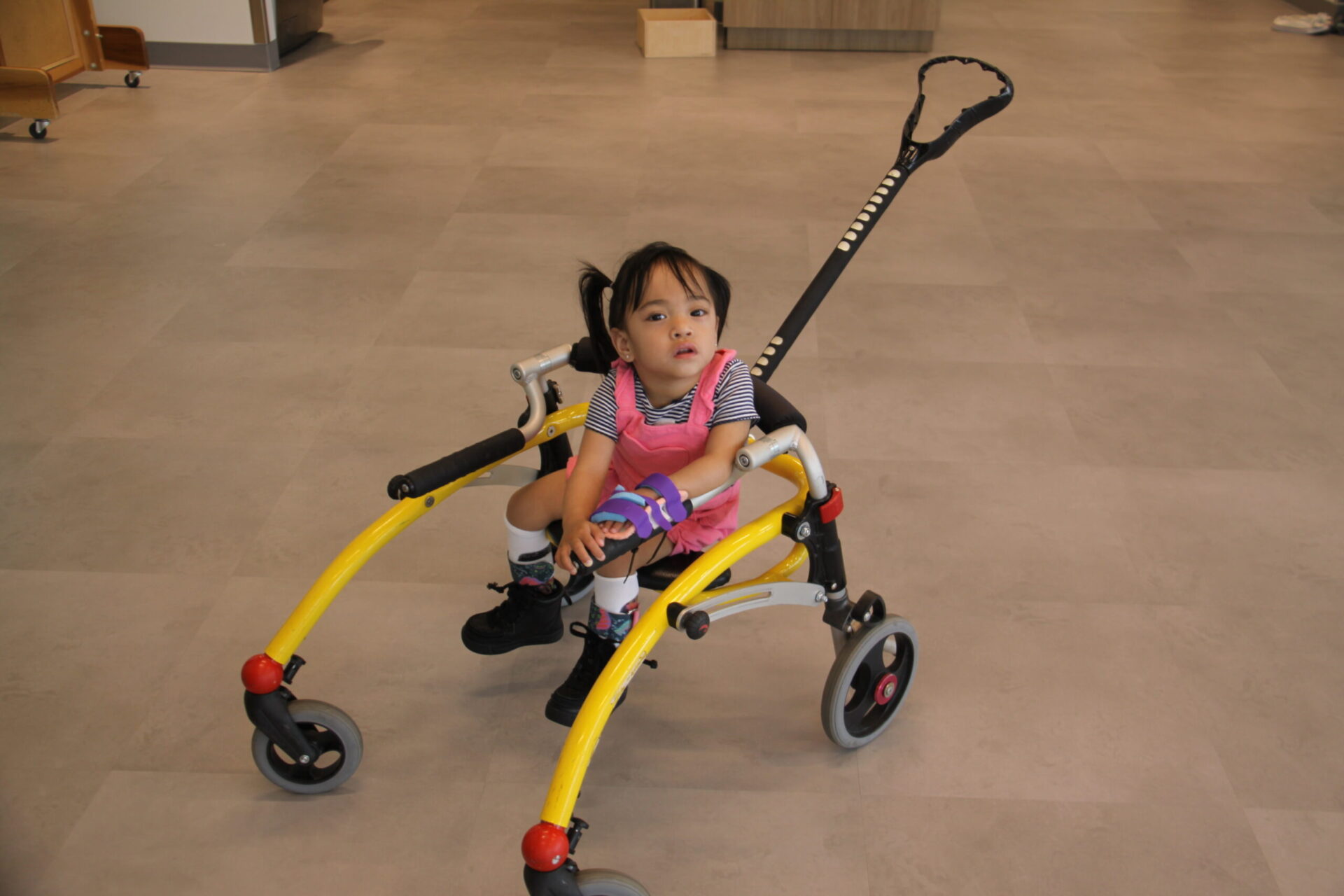

List of Treatments
Functional Strengthening and endurance training on pediatric sized strength equipment
Fitness Training
Stretching
Home Based Programs
Targeting of task-based goals
Motor Planning and Sequencing
Monitor and collaborate on AFO’s and equipment
Cuevas Medek Exercise
Post Surgery and Botox Intervention
Hands-on therapy in an engaging and fun child-friendly environment
Neurodevelopmental Progression
FSCD and PUF therapy
Collaboration with other members of the child’s health team
Teaching children and teens to manage their therapy programs
Autism Spectrum Disorder
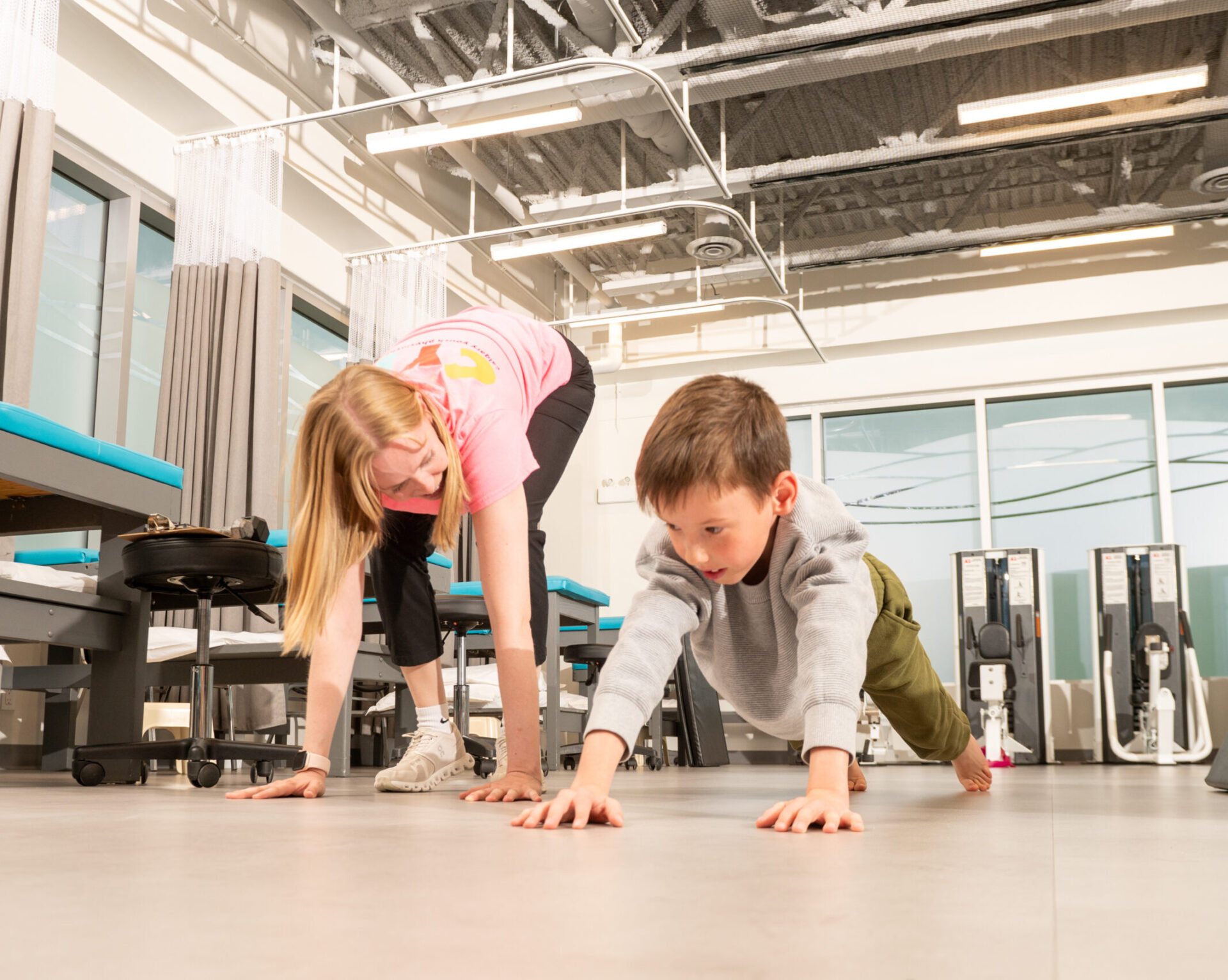
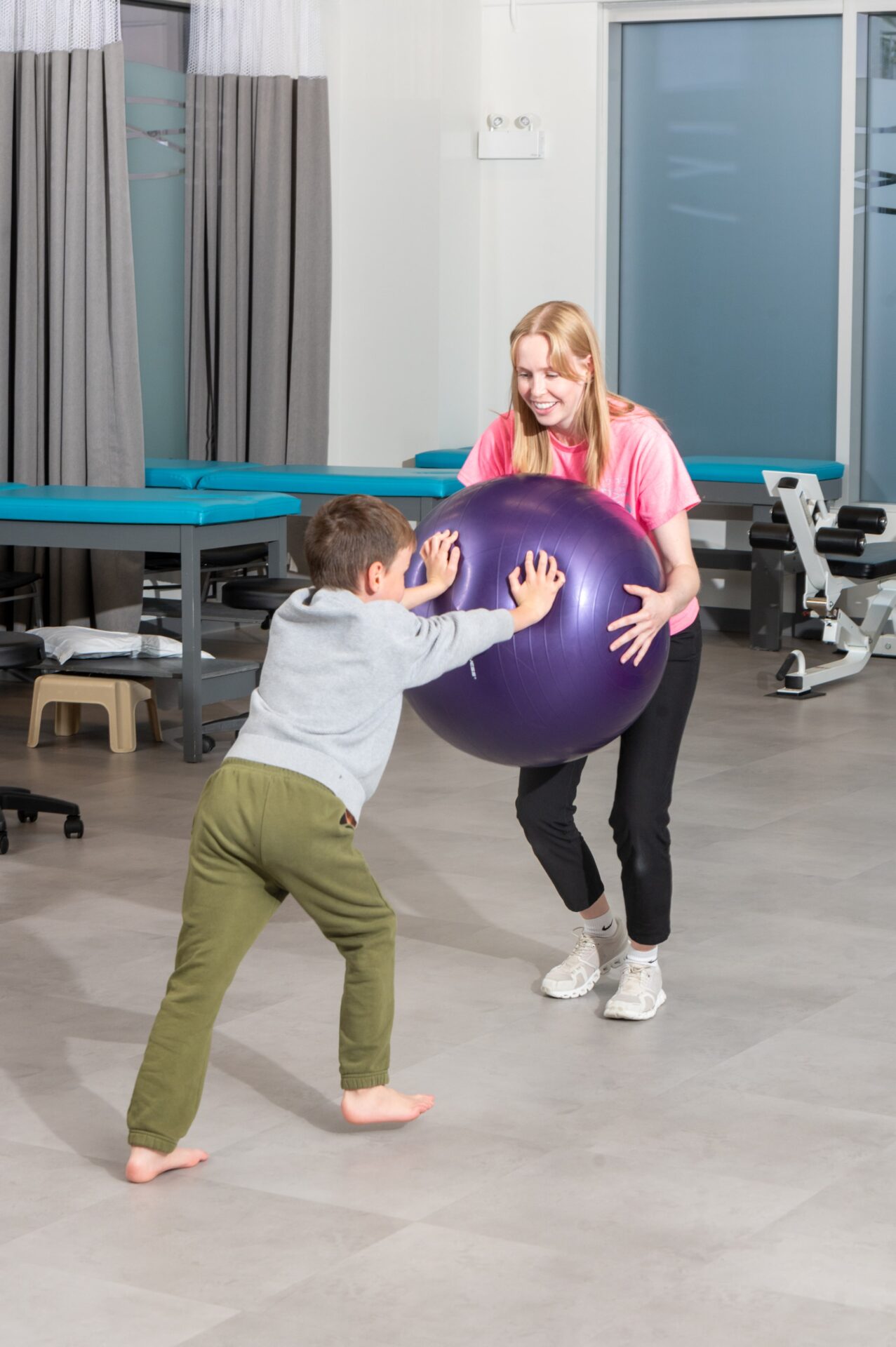
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability that may result in social, communication, and behavioral challenges. Children with ASD will often have impaired motor skills because of low muscle tone, poor balance, a lack of coordination or a combination of all. Motor delays in children with ASD may contribute to difficulty acquiring social skills. Many autistic children have trouble engaging in play-based activities. Early intervention can help children with ASD learn essential skills, improve development and help them meet their full potential. Our team knows how to teach kids with ASD to play and participate in daily routines at home, in the community, and at school to enhance overall well-being, promote participation in daily activities, and address individualized gross motor goals and social engagement for children with ASD.
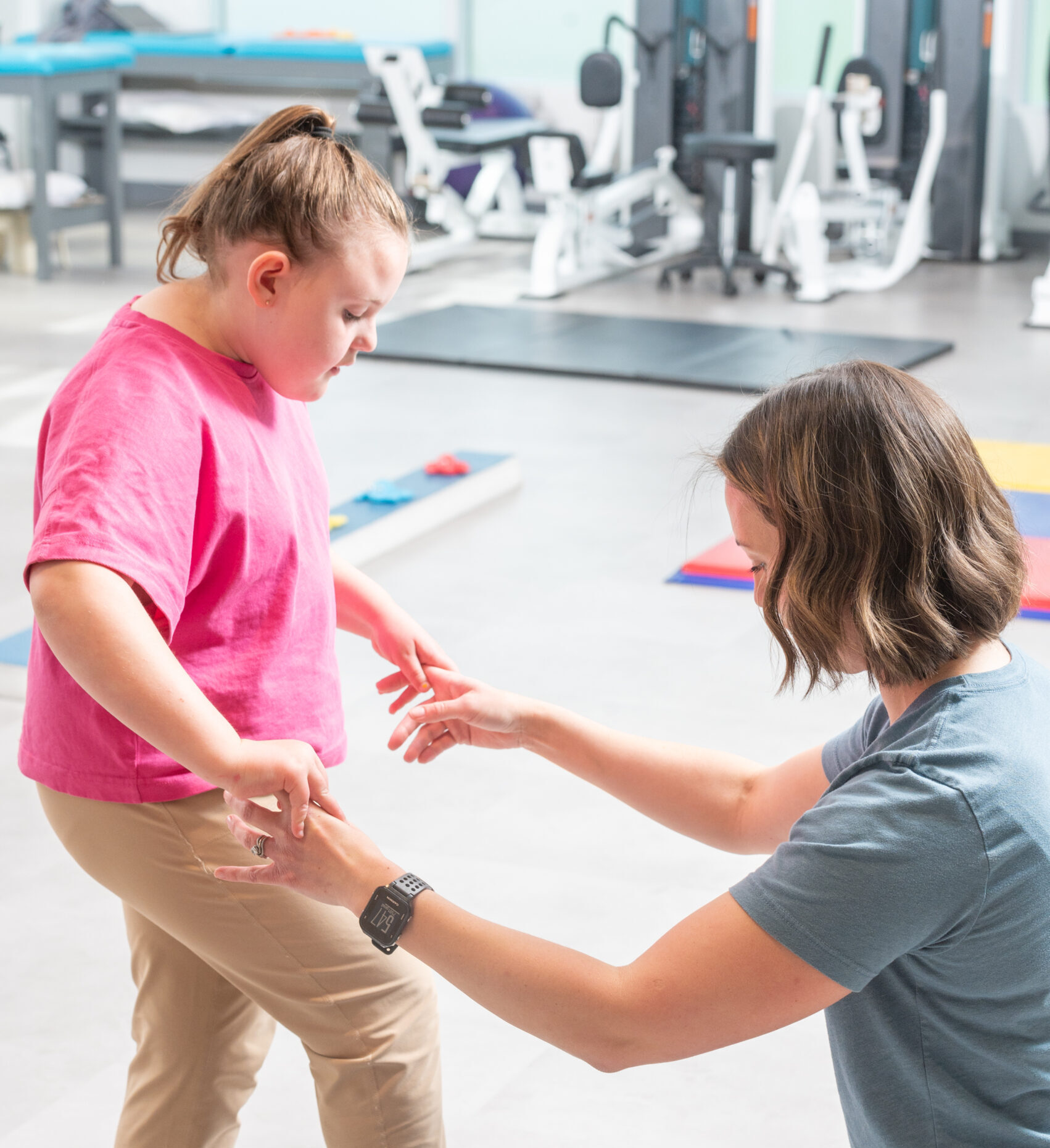

List of Treatments
Treatment based on family-centered goals
Motor skills development
Sensory integration
Development of social recreational skills
Use of a variety of engaging toys and equipment
Collaboration on FSCD teams
Home exercise programs to improve strength, motor planning, ball skills, balance and proprioception
Use of picture schedules during therapy sessions
Advice on appropriate community recreational activities
Developmental Coordination Disorder
A child with Development Coordination Disorder (DCD) may have fine and gross motor skills delays. These movement challenges can affect their education and ability to do everyday tasks, as they may be slow, inaccurate, or inconsistent with fine and gross motor skills. Signs of DCD can vary dramatically from child to child. A diagnosis doesn’t usually happen until preschool age, and it takes careful assessment by a pediatric physiotherapist and developmental pediatrician to identify the disorder and ensure treatment is in line with the child’s goals and needs.

List of Treatments
Custom treatment approach
Goal orientated
Games and home exercise programs that encourage practice, repetition, strengthening, balance and self-coaching strategies
Collaboration with our Occupational therapist
Pre-targeting/practicing sports skills needed for participation in gym at school
Breaking down motor skills and gaining successful practice of individual components
Juvenile Arthritis
Juvenile Arthritis (JA) is the general name for many conditions that cause joint swelling in children under age 16. It is also called juvenile idiopathic arthritis because its cause is unknown. Children with JA often experience joint swelling, pain, and stiffness in the knees, hands, or feet. Other symptoms may include increased tenderness, recurring fever, or a limp without injury. If your child is showing signs of JA, our team has the experience to assess and treat symptoms to help reduce pain and symptoms while helping to prevent long-term joint and muscle damage.
List of Treatments
Gentle stretching and manual therapy and strength training
Symptom management
Exercise prescription
Hot or cold therapy
Recommendation of splints and orthotics
Collaboration with the child's healthcare team
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic diseases that causes progressive weakening and loss of muscle control over time. Children with muscular dystrophy may experience muscle weakness, shortening of muscles, tendons, or other tissues that affect the joints, curvature of the spine, and breathing or heart problems. Symptoms related to muscular dystrophy may contribute to delayed walking, frequent falls, toe walking, and other difficulties with motor function. Children with muscular dystrophy should begin seeing a physio as soon as possible after diagnosis—before joint and muscle tightness develop. Every child will have unique needs based on age, the type of dystrophy they are diagnosed with, and the progression of symptoms.

List of Treatments
Stretching to prevent or reduce muscle contractures.
Gentle muscle strengthening
Introduction of adaptive activities to the child’s environment
Breathing and chest expansion exercises
Collaboration with child’s healthcare team
Monitoring of equipment
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a genetic connective tissue disorder. Individuals with EDS demonstrate defects in the body’s connective tissues, which change their strength, elasticity, integrity, and healing properties. The severity of the syndrome varies greatly depending on the mutation; however, all forms show signs of hypermobility-related issues.
It is usual for young children to be flexible, but the muscles and joints should tighten as they age to protect more challenging movement activities. Children who remain excessively bendy often experience poor core stability, poor coordination, or pain while exercising, leading to an increased risk of sustaining injuries.

List of Treatments
Exercise to build strength and stability around joints.
Postural control training and education
Pain management
Advice on bracing
Education of safe recreational activities
Down Syndrome
Down Syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21. The additional copy changes the typical development of a baby’s brain and body, causing intellectual and physical challenges. Motor development is often delayed in babies with Down Syndrome because they may have low muscle tone, decreased strength and coordination difficulties. Physiotherapy is an important piece of healthcare for children with Down Syndrome.

List of Treatments
Individualized treatment plans
Focus on improving independence with activities of daily living
Therapy focused on improving strength, developmental skills, balance, coordination, posture, and physical fitness.
Advice on shoe wear, orthotics and bracing
Collaboration with other members of the child’s healthcare team
Charcot-Marie Tooth
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is an inherited neurological disorder that affects sensory and motor nerves, causing them to lose their ability to send signals to and from the brain. Without motor signals, muscles weaken, and numbness can occur.
The disease first appears in teens and young adults in its most common forms. Symptoms are all related to muscle weakness or numbness in the hands, forearms, lower legs or feet. Trouble buttoning clothing, holding small objects, cold hands and/or feet, trouble going up and down steps, dragging the feet while walking or trouble with balance may all be signs of the disease. Youth with CMT need to maintain their movement, muscle strength, and flexibility, as it is difficult to build muscle already affected by the disease. Physiotherapy treatment encourages children to stay as active as possible.

List of Treatments
Specialized treatment program
Muscle strengthening, muscle and ligament stretching, stamina training
Balance training
Moderate aerobic exercise to maintain cardiovascular fitness
Exercises to build endurance and help fight fatigue
Advice on bracing

Questions about our clinic?
We have the answers.
Don’t have time to call right now? No worries. Email us. Let’s set up a convenient time for a complimentary 15-minute consultation. Or the answer you’re looking for might be on our Frequently Asked Questions page.

